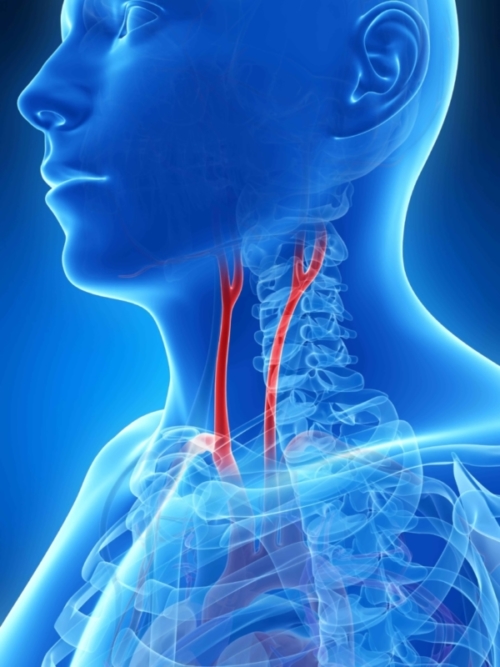
What are Carotid Arteries?
The carotid arteries are located in the neck on each side of the windpipe. They provide important blood flow to the head including the brain. Normally, these arteries have a smooth lining but in diseased vessels, owing to the formation of cholesterol plaque a narrowing develops. This results in deranged blood flow and dislodgement of plaque and other debris, a process called embolisation, that can travel to the brain causing a stroke or transient ischaemic attack (TIA).
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is restricted causing brain cells to die. This may be owing to pressure from bleeding (cerebral haemorrhage) or blockage of an artery in the brain (cerebral infarction). The latter can be caused by carotid artery disease from embolisation or severe restriction of blood flow to the brain.